In non-relativistic kinematics, relative velocity is the vector difference between the velocities of two objects, as evaluated in terms of a single coordinate system.
For example, if the velocities of particles A and B are  and
and 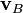 respectively in terms of a given coordinate system, then the relative velocity of A with respect to B (also called the velocity of A relative to B,
respectively in terms of a given coordinate system, then the relative velocity of A with respect to B (also called the velocity of A relative to B, 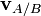 , or
, or  ) is
) is
 and
and 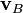 respectively in terms of a given coordinate system, then the relative velocity of A with respect to B (also called the velocity of A relative to B,
respectively in terms of a given coordinate system, then the relative velocity of A with respect to B (also called the velocity of A relative to B, 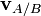 , or
, or  ) is
) is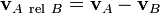 .
.
 .
.
The expression "the velocity of A relative to B" is shorthand for "the velocity of A in the coordinate system where B is always at rest". Read More










No comments:
Post a Comment